C. C. Haggerty and D. Caprioli
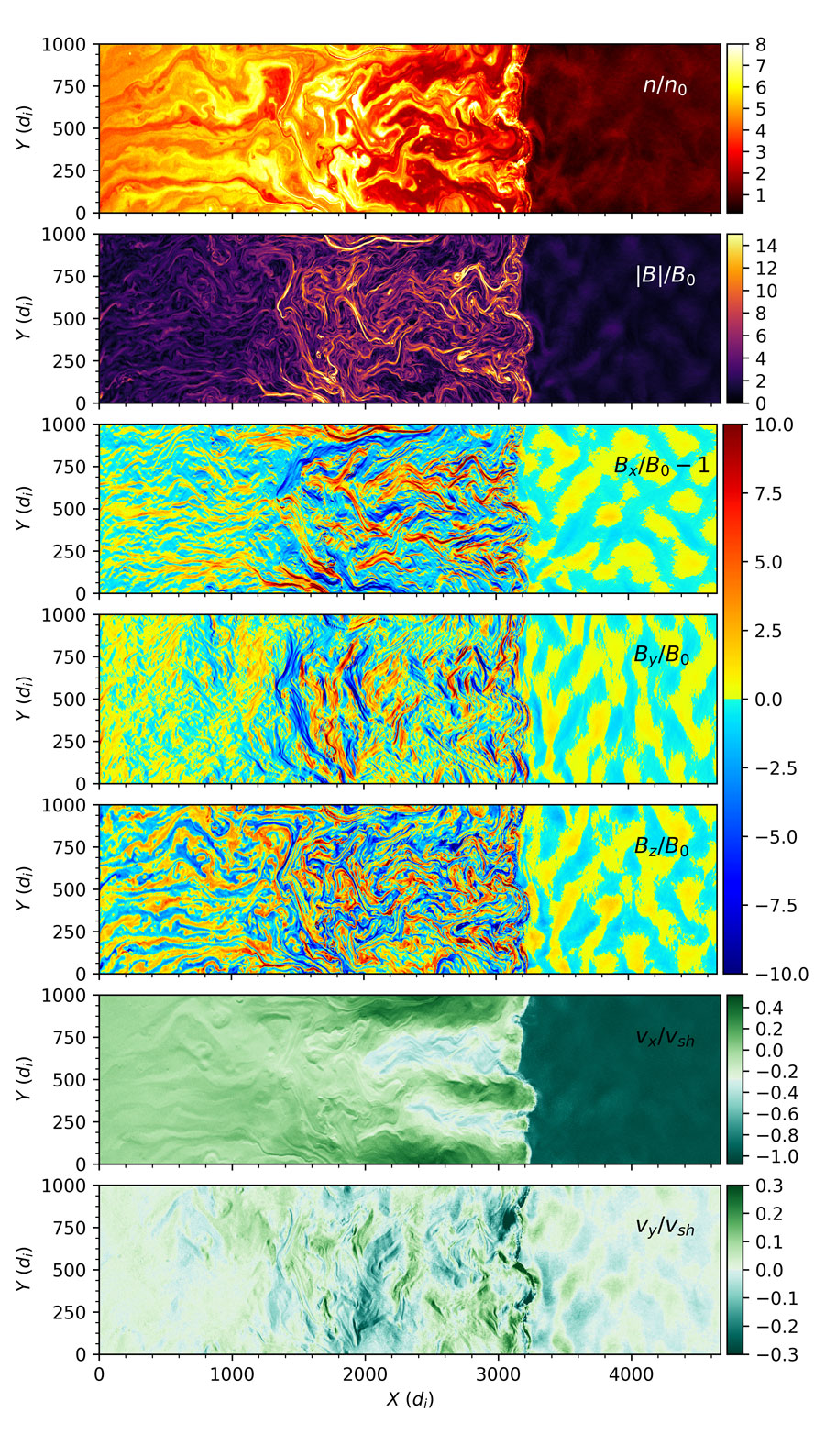
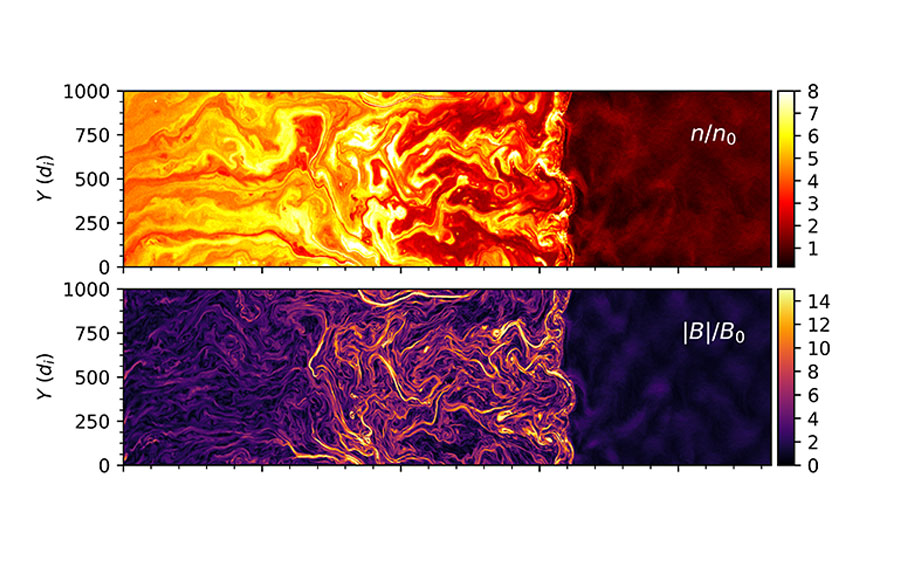
Abstract: We present the first plasma simulations obtained with the code dHybridR, a hybrid particle-in-cell code with fluid electrons and kinetic relativistic ions. dHybridR is perfectly suited for all the astrophysical and space-physics problems where a few energetic non-thermal particles (i.e., Cosmic Rays, CRs) affect the overall dynamics of a non-relativistic plasma, such as CR-driven instabilities, collisionless shocks, magnetic reconnection, turbulence, etc. In this method paper we provide some applications to linear (resonant/non-resonant CR streaming instability) and strongly non-linear (parallel shocks) problems that show the capabilities of the code. In particular, we provide the first self-consistent hybrid runs that show the acceleration of relativistic ions at non-relativistic shocks; CRs develop a power-law in momentum, which translates to a broken power law in energy that exhibits a steepening around the ion rest mass, as predicted by the theory of diffusive shock acceleration. To outline the vast range of possible applications of dHybridR, we show some examples of 2D runs relevant for fast shocks in radio supernovae, whose evolution can be followed in real time, and 3D runs of low-Mach-number heliospheric shocks, which can be compared with in-situ spacecraft observations.
Read the full text on Arxiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.05255
0 Comments